
 AI Researcher & Ph.D Candidate, Yonsei University
AI Researcher & Ph.D Candidate, Yonsei UniversityFederated Learning Multimodal AI Medical Informatics.
I aim to develop robust, trustworthy, and real-world applicable multimodal AI models by leveraging federated learning, which enables collaborative learning across multiple institutions while preserving data privacy.
BiographyI am currently a Ph.D candidate in the Department of Biomedical Systems Informatics at Yonsei University College of Medicine, supervised by Prof. Yu Rang Park. I also working as an AI Researcher at the Digital Healthcare Laboratory (DHLab) in Yonsei University College of Medicine and Severance Hospital in Seoul, Republic of Korea. Previously, I finished my B.B.A in Big Data Management and Statistics at Kookmin University in Seoul, Republic of Korea. From July to September in 2021, I worked as a Data Scientist at DACON, which is the largest data science competition platform in Korea.
Warning
Problem: The current name of your GitHub Pages repository ("Solution: Please consider renaming the repository to "
http://".
However, if the current repository name is intended, you can ignore this message by removing "{% include widgets/debug_repo_name.html %}" in index.html.
Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "Education
-
 Yonsei UniversityDepartment of Biomedical Systems Informatics, College of Medicine
Yonsei UniversityDepartment of Biomedical Systems Informatics, College of Medicine
Ph.D. CandidateSeptember. 2022 - present -
 Kookmin UniversityB.B.A in Big Data Management and StatisticsMarch. 2018 - Febuary. 2022
Kookmin UniversityB.B.A in Big Data Management and StatisticsMarch. 2018 - Febuary. 2022
Research Projects
-
2025-present
-
2024-present
-
2023-2024
-
Artificial Intelligence Learning Data Construction Project
Adolescent and Children Retina Data
funded by - MSIT2022-2022 -
Artificial Intelligence Learning Data Construction Project
Infant Behavior Video Data
funded by - MSIT2022-2022
News
Selected Publications (view all )
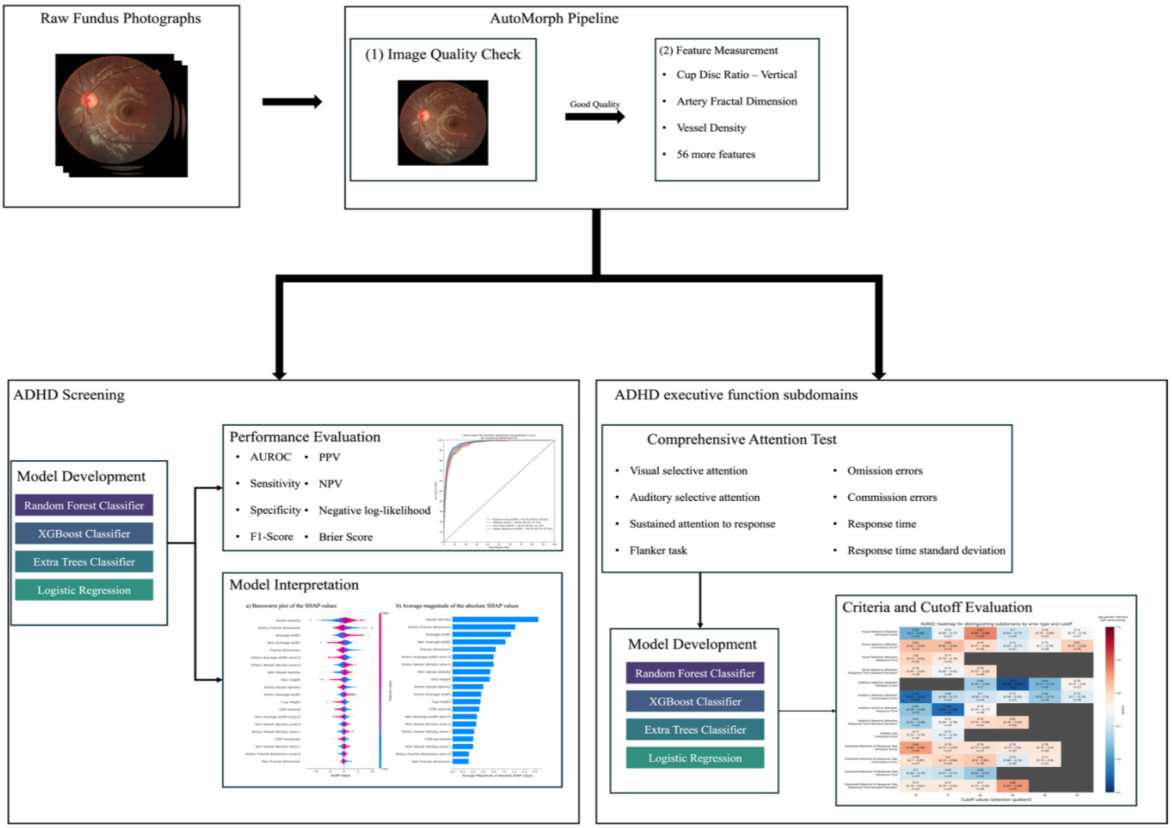
Retinal fundus imaging as biomarker for ADHD using machine learning for screening and visual attention stratification
Hangnyoung Choi*, Hong JaeSeong*, Hyun Goo Kang*, Min-Hyeon Park, Sungji Ha, Junghan Lee, Sangchul Yoon, Daeseong Kim, Yu Rang Park, Keun-Ah Cheon (* equal contribution)
npj Digital Medicine 2025 Medical Dataset Deep+Machine Learning
This study demonstrated that machine learning analysis of retinal fundus photographs can serve as a noninvasive biomarker for screening attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and stratifying executive function deficits, achieving up to 96.9% AUROC and showing strong performance particularly in the visual attention domain.
Retinal fundus imaging as biomarker for ADHD using machine learning for screening and visual attention stratification
Hangnyoung Choi*, Hong JaeSeong*, Hyun Goo Kang*, Min-Hyeon Park, Sungji Ha, Junghan Lee, Sangchul Yoon, Daeseong Kim, Yu Rang Park, Keun-Ah Cheon (* equal contribution)
npj Digital Medicine 2025 Medical Dataset Deep+Machine Learning
This study demonstrated that machine learning analysis of retinal fundus photographs can serve as a noninvasive biomarker for screening attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and stratifying executive function deficits, achieving up to 96.9% AUROC and showing strong performance particularly in the visual attention domain.
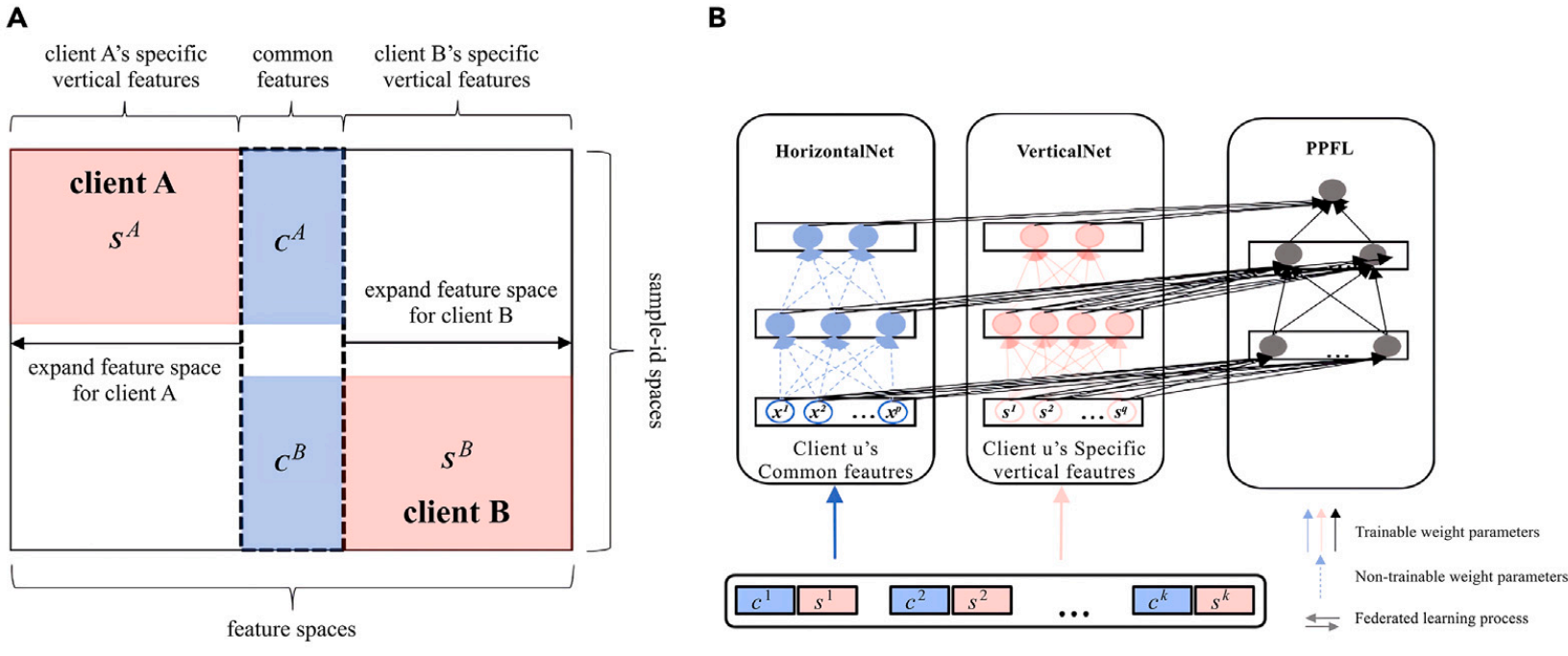
PPFL: A personalized progressive federated learning method for leveraging different healthcare institution-specific features
Tae Hyun Kim*, Jae Yong Yu*, Won Seok Jang, Sun Cheol Heo, MinDong Sung, Hong JaeSeong, KyungSoo Chung, Yu Rang Park (* equal contribution)
iScience 2024 Medical Dataset Federated Learning
This study proposes a personalized progressive federated learning (PPFL) framework that incorporates client-specific feature information for heterogeneous healthcare data, achieving superior mortality prediction performance (accuracy = 0.941, AUROC = 0.948) compared with local and FedAvg models, and demonstrating the utility of personalized FL for vertically distributed clinical features.
PPFL: A personalized progressive federated learning method for leveraging different healthcare institution-specific features
Tae Hyun Kim*, Jae Yong Yu*, Won Seok Jang, Sun Cheol Heo, MinDong Sung, Hong JaeSeong, KyungSoo Chung, Yu Rang Park (* equal contribution)
iScience 2024 Medical Dataset Federated Learning
This study proposes a personalized progressive federated learning (PPFL) framework that incorporates client-specific feature information for heterogeneous healthcare data, achieving superior mortality prediction performance (accuracy = 0.941, AUROC = 0.948) compared with local and FedAvg models, and demonstrating the utility of personalized FL for vertically distributed clinical features.
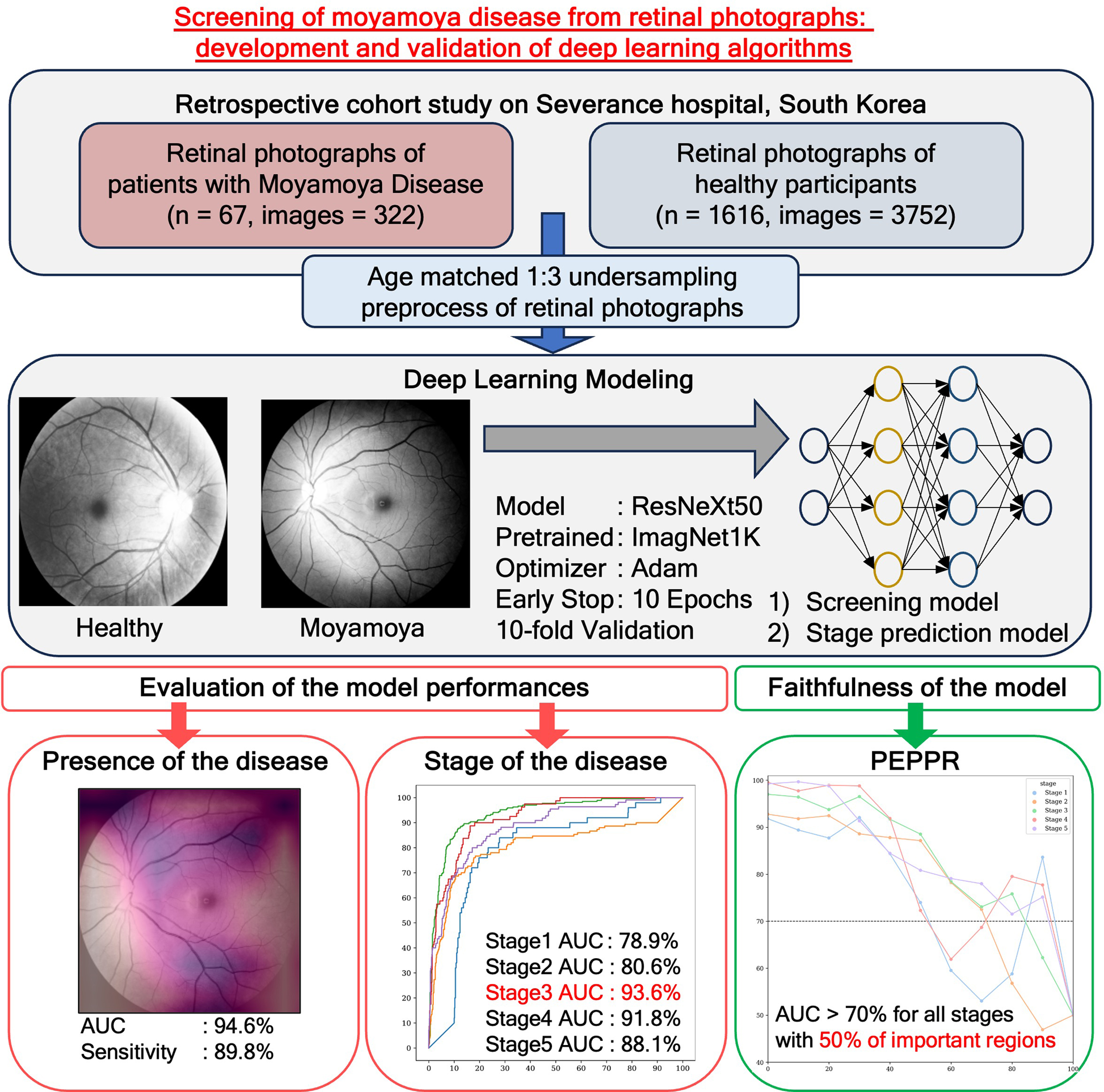
Screening of Moyamoya Disease From Retinal Photographs: Development and Validation of Deep Learning Algorithms
Hong JaeSeong*, Sangchul Yoon*, Kyu Won Shim, Yu Rang Park (* equal contribution)
Stroke 2024 Medical Dataset Deep Learning
This study developed a deep learning model using retinal fundus photographs to screen for and stage Moyamoya disease (MMD), achieving high diagnostic performance (AUROC = 94.6%) and identifying retinal vascular regions as key features, suggesting that retinal imaging may serve as a noninvasive biomarker for MMD detection and progression assessment.
Screening of Moyamoya Disease From Retinal Photographs: Development and Validation of Deep Learning Algorithms
Hong JaeSeong*, Sangchul Yoon*, Kyu Won Shim, Yu Rang Park (* equal contribution)
Stroke 2024 Medical Dataset Deep Learning
This study developed a deep learning model using retinal fundus photographs to screen for and stage Moyamoya disease (MMD), achieving high diagnostic performance (AUROC = 94.6%) and identifying retinal vascular regions as key features, suggesting that retinal imaging may serve as a noninvasive biomarker for MMD detection and progression assessment.