2025
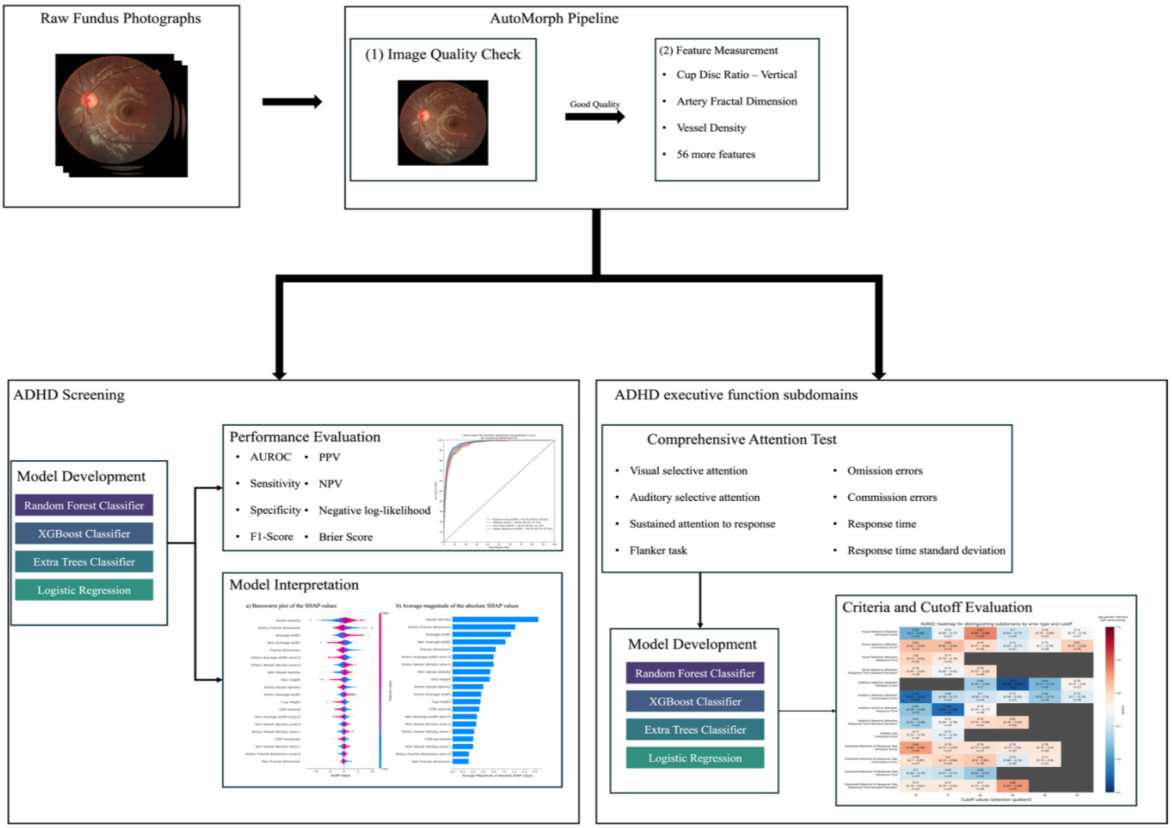
Retinal fundus imaging as biomarker for ADHD using machine learning for screening and visual attention stratification
Hangnyoung Choi*, Hong JaeSeong*, Hyun Goo Kang*, Min-Hyeon Park, Sungji Ha, Junghan Lee, Sangchul Yoon, Daeseong Kim, Yu Rang Park, Keun-Ah Cheon (* equal contribution)
npj Digital Medicine 2025 Medical Dataset Deep+Machine Learning
This study demonstrated that machine learning analysis of retinal fundus photographs can serve as a noninvasive biomarker for screening attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and stratifying executive function deficits, achieving up to 96.9% AUROC and showing strong performance particularly in the visual attention domain.
Retinal fundus imaging as biomarker for ADHD using machine learning for screening and visual attention stratification
Hangnyoung Choi*, Hong JaeSeong*, Hyun Goo Kang*, Min-Hyeon Park, Sungji Ha, Junghan Lee, Sangchul Yoon, Daeseong Kim, Yu Rang Park, Keun-Ah Cheon (* equal contribution)
npj Digital Medicine 2025 Medical Dataset Deep+Machine Learning
This study demonstrated that machine learning analysis of retinal fundus photographs can serve as a noninvasive biomarker for screening attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and stratifying executive function deficits, achieving up to 96.9% AUROC and showing strong performance particularly in the visual attention domain.
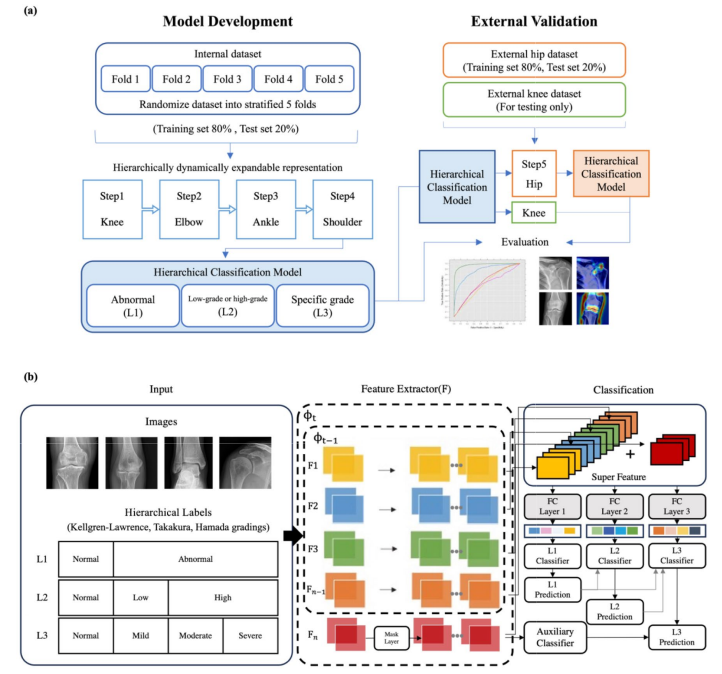
Classification models for arthropathy grades of multiple joints based on hierarchical continual learning
Bong Kyung Jang, Shiwon Kim, Jae Yong Yu, Hong JaeSeong, Hee Woo Cho, Hong Seon Lee, Jiwoo Park, Jeesoo Woo, Young Han Lee, Yu Rang Park
La radiologia medica 2025 Medical Dataset Continual Learning
This study proposed a Hierarchical Dynamically Expandable Representation (Hi-DER) model for continual arthropathy classification across multiple joints, achieving high diagnostic performance (AUC up to 0.994) and strong generalization in external validation, suggesting its potential for scalable, multi-joint musculoskeletal disease assessment.
Classification models for arthropathy grades of multiple joints based on hierarchical continual learning
Bong Kyung Jang, Shiwon Kim, Jae Yong Yu, Hong JaeSeong, Hee Woo Cho, Hong Seon Lee, Jiwoo Park, Jeesoo Woo, Young Han Lee, Yu Rang Park
La radiologia medica 2025 Medical Dataset Continual Learning
This study proposed a Hierarchical Dynamically Expandable Representation (Hi-DER) model for continual arthropathy classification across multiple joints, achieving high diagnostic performance (AUC up to 0.994) and strong generalization in external validation, suggesting its potential for scalable, multi-joint musculoskeletal disease assessment.
2024
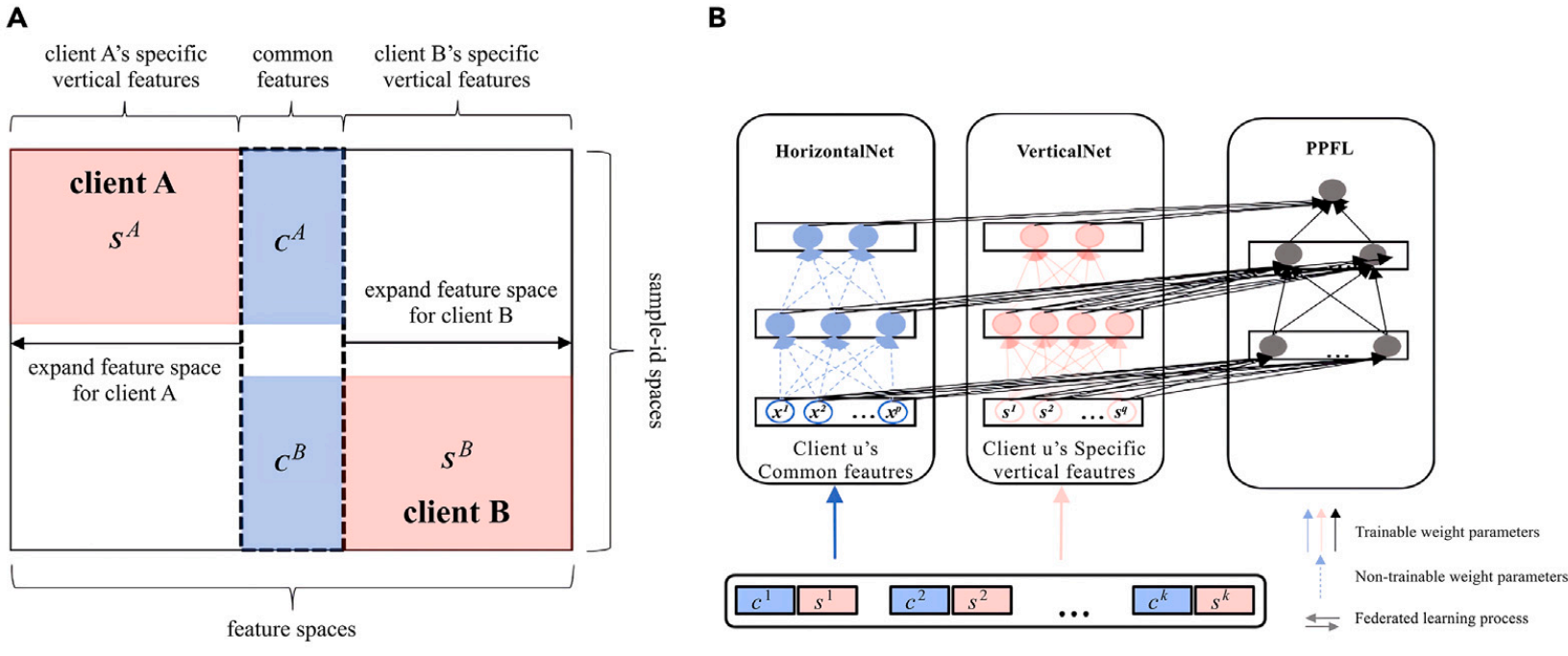
PPFL: A personalized progressive federated learning method for leveraging different healthcare institution-specific features
Tae Hyun Kim*, Jae Yong Yu*, Won Seok Jang, Sun Cheol Heo, MinDong Sung, Hong JaeSeong, KyungSoo Chung, Yu Rang Park (* equal contribution)
iScience 2024 Medical Dataset Federated Learning
This study proposes a personalized progressive federated learning (PPFL) framework that incorporates client-specific feature information for heterogeneous healthcare data, achieving superior mortality prediction performance (accuracy = 0.941, AUROC = 0.948) compared with local and FedAvg models, and demonstrating the utility of personalized FL for vertically distributed clinical features.
PPFL: A personalized progressive federated learning method for leveraging different healthcare institution-specific features
Tae Hyun Kim*, Jae Yong Yu*, Won Seok Jang, Sun Cheol Heo, MinDong Sung, Hong JaeSeong, KyungSoo Chung, Yu Rang Park (* equal contribution)
iScience 2024 Medical Dataset Federated Learning
This study proposes a personalized progressive federated learning (PPFL) framework that incorporates client-specific feature information for heterogeneous healthcare data, achieving superior mortality prediction performance (accuracy = 0.941, AUROC = 0.948) compared with local and FedAvg models, and demonstrating the utility of personalized FL for vertically distributed clinical features.
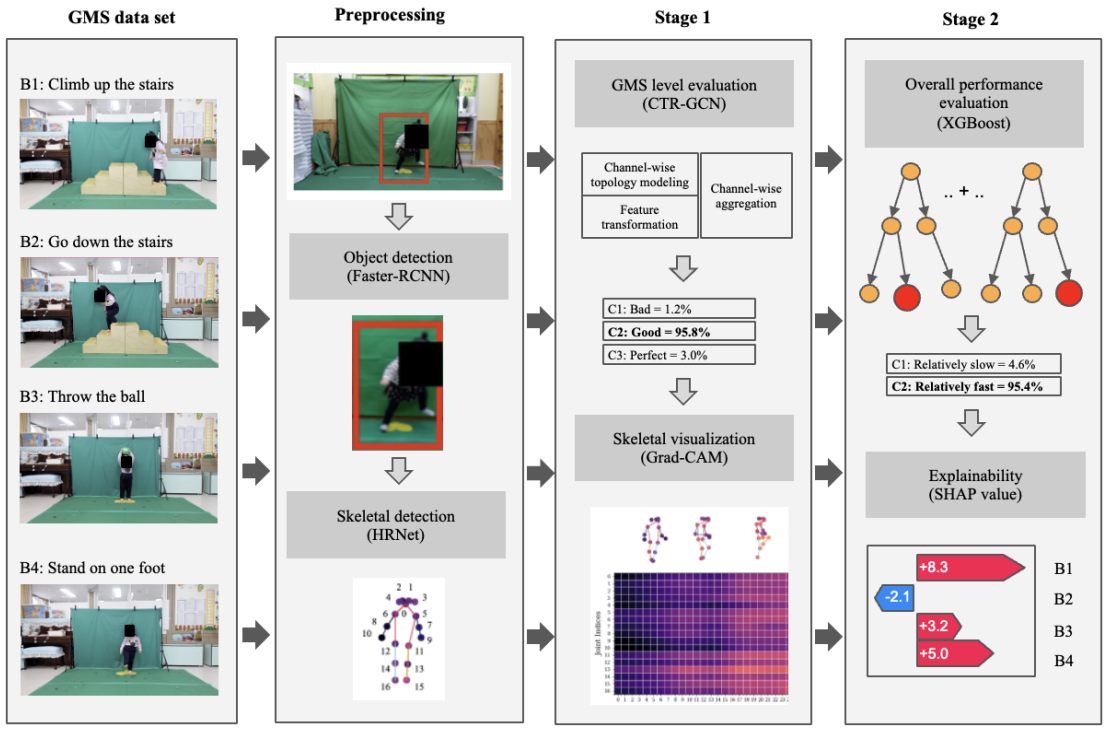
Comprehensive Assessment and Early Prediction of Gross Motor Performance in Toddlers With Graph Convolutional Networks–Based Deep Learning: Development and Validation Study
Sulim Chun*, Sooyoung Jang*, Jin Yong Kim, Chanyoung Ko, JooHyun Lee, Hong JaeSeong, Yu Rang Park (* equal contribution)
JMIR Formative Research 2024 Medical Dataset Deep+Machine Learning
This study developed a deep learning model using retinal fundus photographs to screen for and stage Moyamoya disease (MMD), achieving high diagnostic performance (AUROC = 94.6%) and identifying retinal vascular regions as key features, suggesting that retinal imaging may serve as a noninvasive biomarker for MMD detection and progression assessment.
Comprehensive Assessment and Early Prediction of Gross Motor Performance in Toddlers With Graph Convolutional Networks–Based Deep Learning: Development and Validation Study
Sulim Chun*, Sooyoung Jang*, Jin Yong Kim, Chanyoung Ko, JooHyun Lee, Hong JaeSeong, Yu Rang Park (* equal contribution)
JMIR Formative Research 2024 Medical Dataset Deep+Machine Learning
This study developed a deep learning model using retinal fundus photographs to screen for and stage Moyamoya disease (MMD), achieving high diagnostic performance (AUROC = 94.6%) and identifying retinal vascular regions as key features, suggesting that retinal imaging may serve as a noninvasive biomarker for MMD detection and progression assessment.
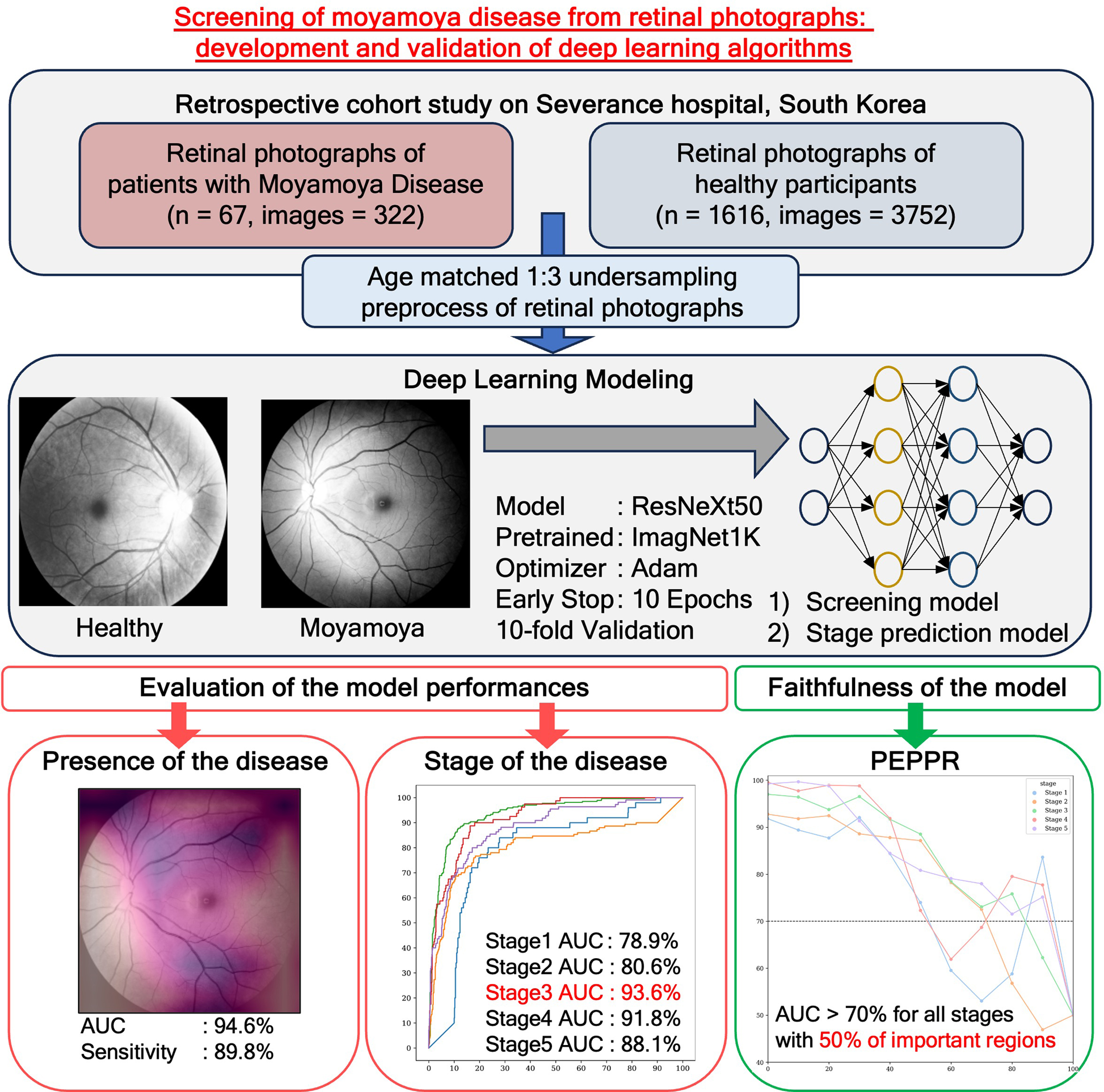
Screening of Moyamoya Disease From Retinal Photographs: Development and Validation of Deep Learning Algorithms
Hong JaeSeong*, Sangchul Yoon*, Kyu Won Shim, Yu Rang Park (* equal contribution)
Stroke 2024 Medical Dataset Deep Learning
This study developed a deep learning model using retinal fundus photographs to screen for and stage Moyamoya disease (MMD), achieving high diagnostic performance (AUROC = 94.6%) and identifying retinal vascular regions as key features, suggesting that retinal imaging may serve as a noninvasive biomarker for MMD detection and progression assessment.
Screening of Moyamoya Disease From Retinal Photographs: Development and Validation of Deep Learning Algorithms
Hong JaeSeong*, Sangchul Yoon*, Kyu Won Shim, Yu Rang Park (* equal contribution)
Stroke 2024 Medical Dataset Deep Learning
This study developed a deep learning model using retinal fundus photographs to screen for and stage Moyamoya disease (MMD), achieving high diagnostic performance (AUROC = 94.6%) and identifying retinal vascular regions as key features, suggesting that retinal imaging may serve as a noninvasive biomarker for MMD detection and progression assessment.
2023
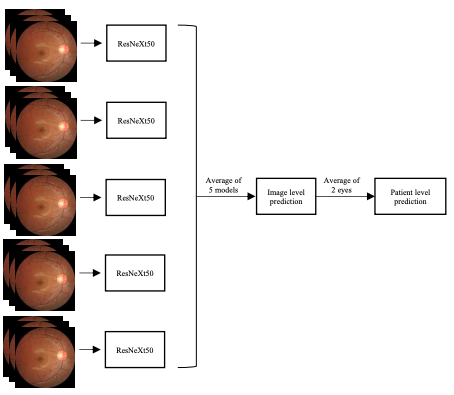
Development of deep ensembles for screening and severity of autism using retinal photographs
Jae Han Kim*, Hong JaeSeong*, Hangnyoung Choi*, Hyun Goo Kang*, Sangchul Yoon, Jung Yeon Hwang, Yu Rang Park, Keun-Ah Cheon (* equal contribution)
JAMA Network Open. 2023 Medical Dataset Deep Ensemble
This study developed deep learning models using retinal fundus photographs to screen for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and assess symptom severity, achieving perfect diagnostic accuracy for ASD detection and demonstrating the optic disc as a key biomarker for objective, accessible ASD screening.
Development of deep ensembles for screening and severity of autism using retinal photographs
Jae Han Kim*, Hong JaeSeong*, Hangnyoung Choi*, Hyun Goo Kang*, Sangchul Yoon, Jung Yeon Hwang, Yu Rang Park, Keun-Ah Cheon (* equal contribution)
JAMA Network Open. 2023 Medical Dataset Deep Ensemble
This study developed deep learning models using retinal fundus photographs to screen for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and assess symptom severity, achieving perfect diagnostic accuracy for ASD detection and demonstrating the optic disc as a key biomarker for objective, accessible ASD screening.
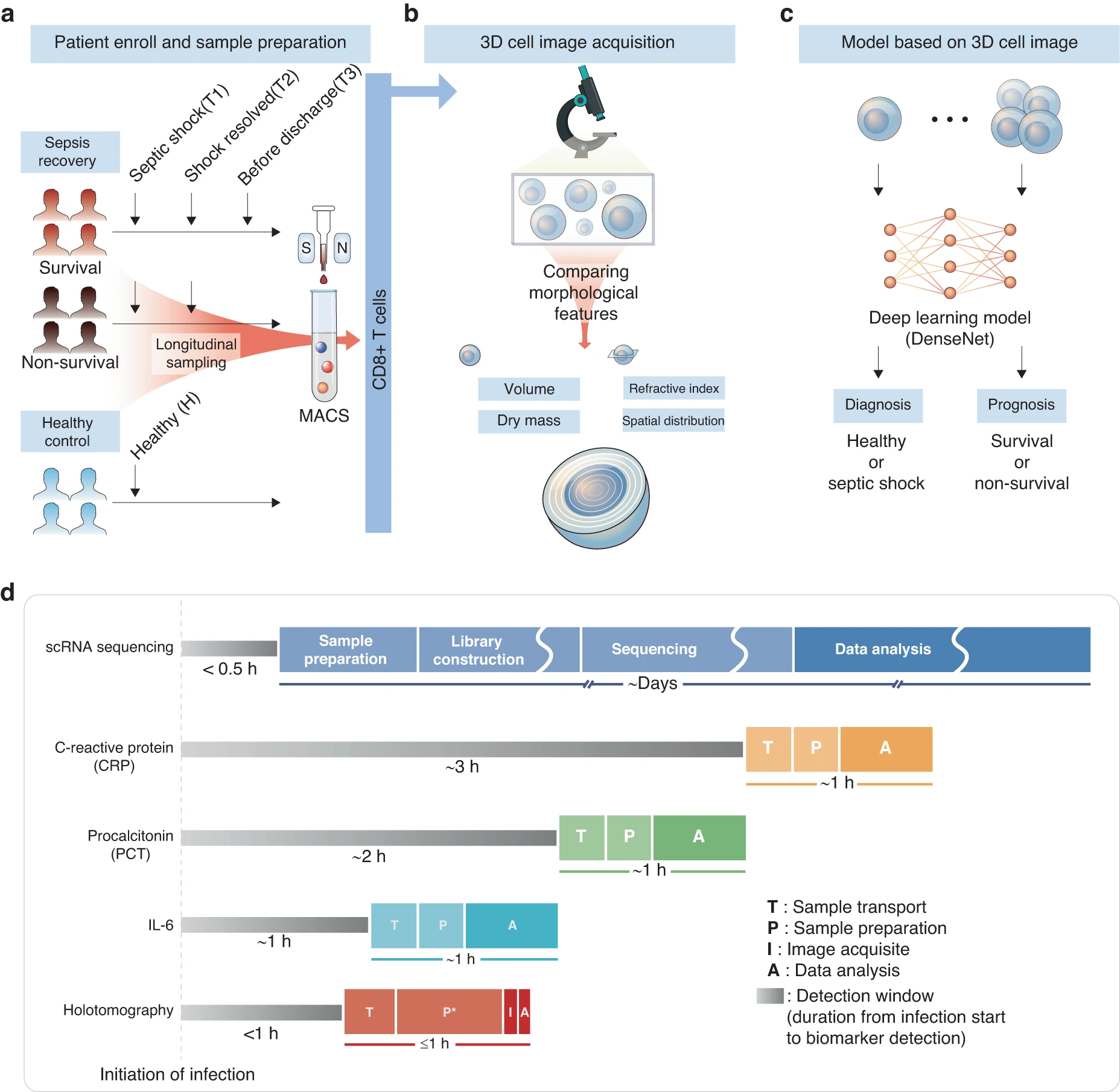
Three-dimensional label-free morphology of CD8+ T cells as a sepsis biomarker
MinDong Sung*, Jong Hyun Kim*, Hyun-Seok Min*, Sooyoung Jang, Hong JaeSeong, Bo Kyu Choi, JuHye Shin, Kyung Soo Chung, Yu Rang Park (* equal contribution)
Light Science & Applications 2023 Medical Dataset Deep Learning
This study shows that three-dimensional label-free CD8⁺ T cell morphology can serve as a rapid and minimally invasive biomarker for sepsis diagnosis and prognosis, with a deep learning model achieving near-perfect accuracy and revealing strong correlations between cellular morphology and clinical indices.
Three-dimensional label-free morphology of CD8+ T cells as a sepsis biomarker
MinDong Sung*, Jong Hyun Kim*, Hyun-Seok Min*, Sooyoung Jang, Hong JaeSeong, Bo Kyu Choi, JuHye Shin, Kyung Soo Chung, Yu Rang Park (* equal contribution)
Light Science & Applications 2023 Medical Dataset Deep Learning
This study shows that three-dimensional label-free CD8⁺ T cell morphology can serve as a rapid and minimally invasive biomarker for sepsis diagnosis and prognosis, with a deep learning model achieving near-perfect accuracy and revealing strong correlations between cellular morphology and clinical indices.
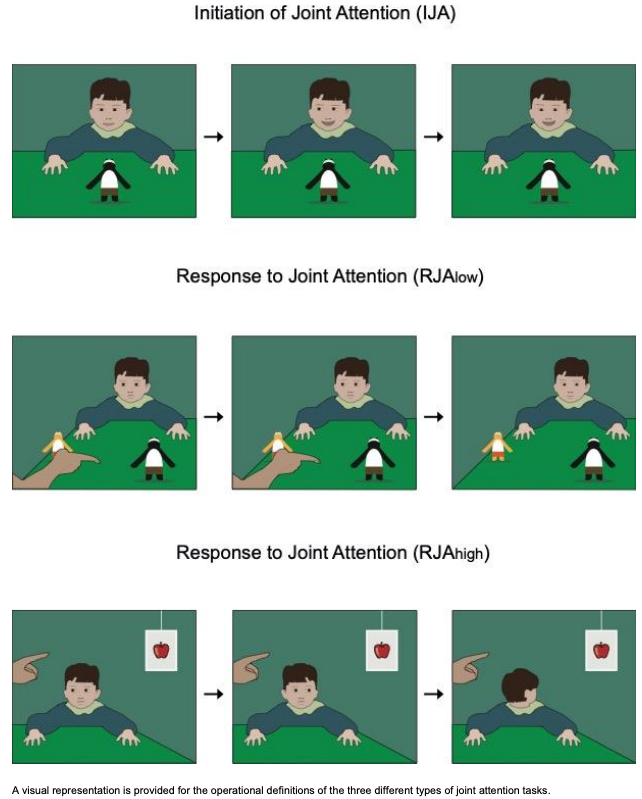
Development and Validation of a Joint Attention-Based Deep Learning System for Detection and Symptom Severity Assessment of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Chanyoung Ko*, Jae-Hyun Lim*, Hong JaeSeong, Soon-Beom Hong, Yu Rang Park (* equal contribution)
JAMA Network Open. 2023 Medical Dataset Deep Learning
This study developed deep learning models that analyze video-based joint attention behaviors to distinguish children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) from typically developing peers and to assess ASD symptom severity, achieving high diagnostic accuracy and demonstrating the feasibility of objective digital measurement of joint attention.
Development and Validation of a Joint Attention-Based Deep Learning System for Detection and Symptom Severity Assessment of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Chanyoung Ko*, Jae-Hyun Lim*, Hong JaeSeong, Soon-Beom Hong, Yu Rang Park (* equal contribution)
JAMA Network Open. 2023 Medical Dataset Deep Learning
This study developed deep learning models that analyze video-based joint attention behaviors to distinguish children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) from typically developing peers and to assess ASD symptom severity, achieving high diagnostic accuracy and demonstrating the feasibility of objective digital measurement of joint attention.